Muscle Cell
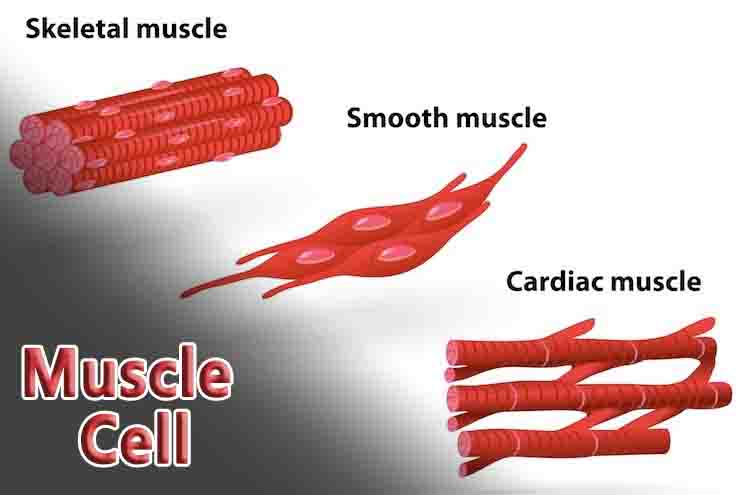
Muscle Cell Definition A muscle cell, or myocyte, is a specialized animal cell that can shorten its length by using a series of motor proteins. In addition to several other associated proteins, actin and myosin form filaments that slide past each other to contract muscle cells. They are called sarcomeres, and they run end-to-end within … Read more